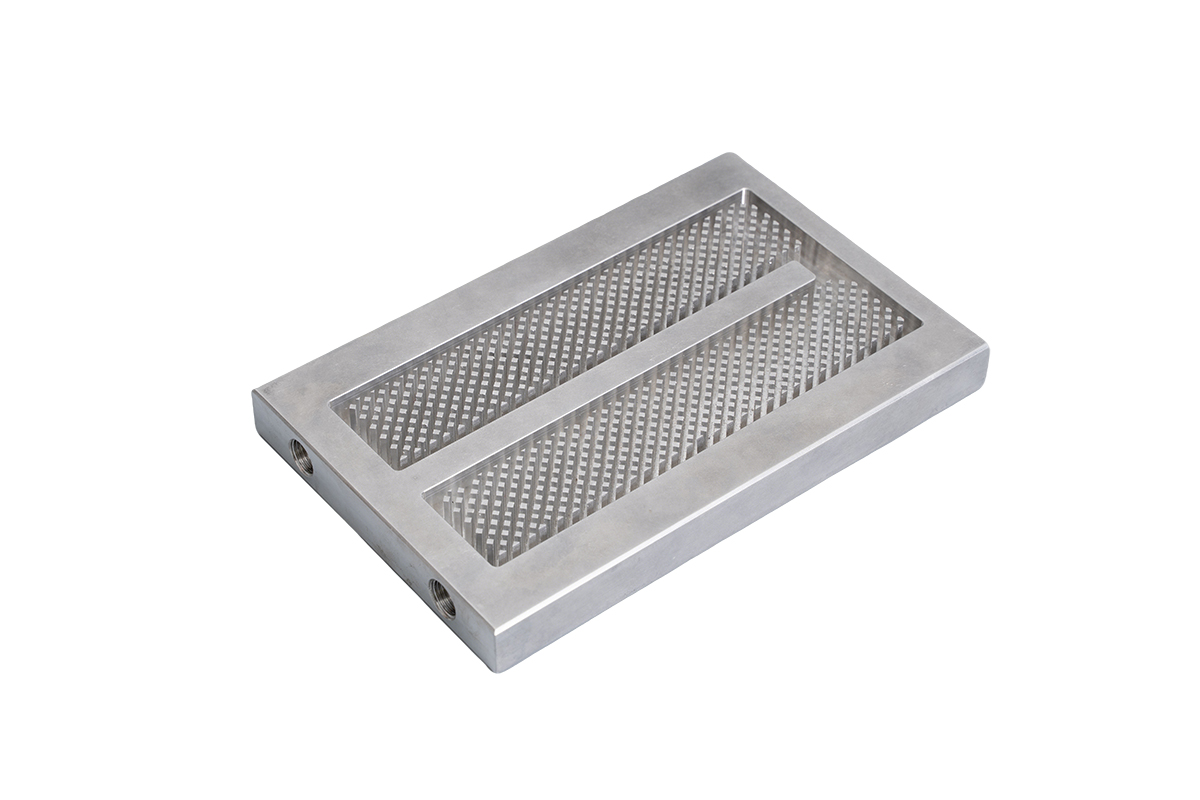



A Brazed Liquid Cold Plate is a high-efficiency thermal management solution designed for applications where air cooling or conventional cooling plates can no longer meet heat dissipation requirements. By using brazing technology to permanently bond internal flow structures, brazed cold plates deliver excellent thermal performance, high structural integrity, and long-term leak resistance.
Compared with machined or mechanically assembled cold plates, brazed liquid cold plates enable more complex internal channel designs, making them ideal for high power density cooling, compact system layouts, and demanding industrial environments.
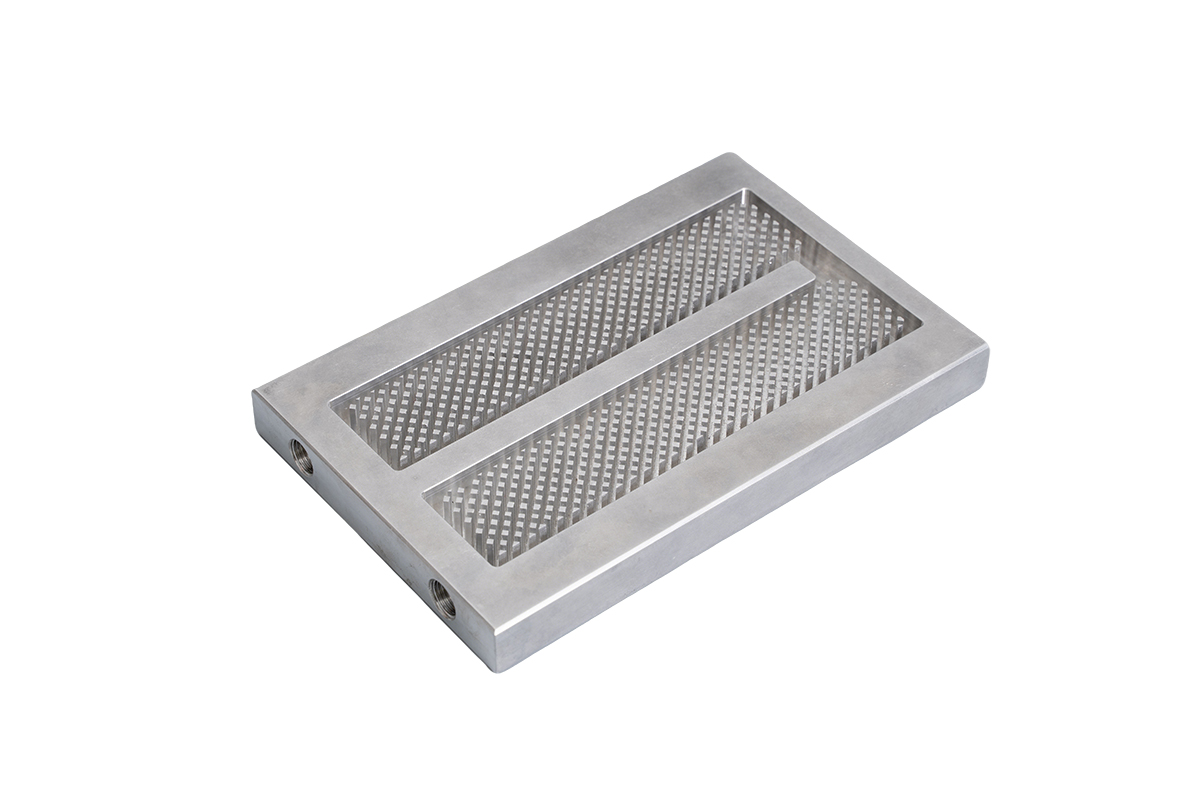

A brazed cold plate is a type of liquid cooling plate manufactured by joining multiple metal components—typically aluminum—using a controlled brazing process. During brazing, filler metal melts and bonds the components together without melting the base material, forming sealed internal channels for coolant flow.
This method allows the creation of:
Multi-layer channel structures
High-density fin or microchannel designs
Uniform internal flow paths
As a result, brazed aluminum cold plates achieve lower thermal resistance and more uniform temperature distribution than many traditional cooling plates.
Cold plate cooling using brazed construction follows a direct and efficient heat transfer path:
Heat is conducted from the heat source into the cold plate base.
Coolant flows through brazed internal channels, absorbing thermal energy.
Heat is carried away by the liquid to a heat exchanger or chiller.
Cooled liquid recirculates through the system.
Because liquid has a much higher heat capacity than air, water cooled cold plates and liquid cold plate cooling systems are particularly effective for electronics, batteries, and power modules operating under continuous high loads.
Brazing enables tight thermal contact between the base plate and internal flow structures, minimizing thermal resistance and improving heat transfer efficiency.
Vacuum brazing or controlled atmosphere brazing (CAB) produces fully metallurgical joints, resulting in leak-resistant cold plates suitable for long-term operation and elevated pressures.
Brazed construction supports:
Multi-pass designs (2 pass, 4 pass, 6 pass cold plates)
Multi-circuit layouts (7 circuit, 8 circuit, 10 circuit cold plates)
Microchannel and high-surface-area flow paths
Once tooling is established, brazed cold plates offer excellent repeatability and cost efficiency for medium to high production volumes.
Most brazed cold plates are manufactured from aluminum due to its balance of thermal conductivity, weight, and cost.
Aluminum brazed cold plate – most common, lightweight, cost-effective
Copper brazed cold plate – higher thermal conductivity for extreme heat flux
Stainless steel brazed cold plate – specialized applications requiring corrosion resistance
Among these, brazed aluminum cooling plates are the industry standard for EV, data center, and power electronics applications.
| Parameter | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| Plate Material | Aluminum (AA3003 / AA6061) |
| Brazing Process | Vacuum Brazing / CAB Brazing |
| Cooling Medium | Water / Water-Glycol |
| Max Operating Pressure | 1.5 – 3.0 MPa |
| Max Heat Dissipation | Up to 500 W/cm² (design dependent) |
| Channel Type | Multi-channel / Microchannel |
| Flow Configuration | Single pass / Multi-pass / Multi-circuit |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 120°C |
| Surface Flatness | ≤ 0.05 mm |
| Leakage Rate | < 1 × 10⁻⁶ mbar·L/s |
Specifications may vary based on custom design requirements.
| Feature | Brazed Cold Plate | Machined Cold Plate | FSW Cold Plate | Tubed Cold Plate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Performance | ★★★★★ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ |
| Channel Complexity | Very High | Medium | Medium | Low |
| Leak Resistance | Excellent | Good | Excellent | Medium |
| Production Scalability | High | Low | Medium | High |
| Unit Cost (Volume) | Medium | High | Medium | Low |
| Typical Applications | EV, Data Center, Power Electronics | Prototypes, Low Volume | Large Aluminum Plates | Industrial Cooling |
Brazed liquid cold plates offer the best balance of performance, reliability, and scalability for high-power applications.
Brazed cold plates are widely used in:
EV battery thermal management systems
Power electronics (IGBT, MOSFET, inverters)
Data center servers and CDU systems
Energy storage systems (ESS)
Industrial laser and automation equipment
In these environments, custom brazed liquid cold plates ensure stable operating temperatures and extended component lifespan.
Standard designs cannot always meet specific system requirements. Our custom cold plate solutions are engineered based on:
Heat load and heat flux distribution
Available flow rate and pump pressure
Installation space and mounting interface
Temperature uniformity targets
System integration with chillers or heat exchangers
From concept and simulation to brazed manufacturing and testing, custom solutions deliver optimal performance and reliability.
When applications demand:
High heat dissipation in compact spaces
Long-term leak-free operation
Uniform temperature control
Scalable production with consistent quality
Brazed liquid cold plates are the preferred solution over conventional cooling plate technologies.
A Brazed Liquid Cold Plate is a type of liquid cold plate manufactured by brazing multiple metal layers together to form sealed internal flow channels. Compared with tubed cold plates, brazed cold plates offer higher structural integrity, better thermal performance, and more compact channel design, making them ideal for high-power liquid cooling applications.
Commonly used materials include aluminum cold plate, stainless steel cold plate, and copper cold plate, depending on thermal, corrosion, and pressure requirements.
A brazed liquid cold plate works by circulating coolant—typically water or water-glycol—through internal brazed flow circuits. Heat generated by electronic components is transferred through the plate material into the coolant and then carried away by the cold plate cooling system.
Because the channels are fully brazed rather than mechanically sealed, heat transfer efficiency is higher and leakage risk is significantly reduced.
Compared to tubed cold plates or mechanically assembled cooling plates, brazed liquid cold plates provide:
Higher heat flux capability
Better pressure resistance
More uniform cooling across large cold plates
Compact internal microchannel or multi-circuit designs
Improved reliability for long-term operation
These advantages make brazed cold plates suitable for liquid cold plate cooling in data centers, automotive electronics, energy storage, and industrial power systems.
We offer brazed liquid cold plates in multiple materials:
Aluminum cooling plate – lightweight, cost-effective, widely used
Copper cold plate – excellent thermal conductivity for high heat loads
Stainless steel cooling plate – corrosion resistance and high-pressure tolerance
Material selection depends on thermal requirements, coolant type, operating pressure, and application environment.
Yes. We specialize in custom liquid cold plates tailored to specific applications. Customization options include:
Plate dimensions (small cold plate or large cold plate)
Flow path design (2 pass cold plate, 4 pass cold plate, 6 pass cold plate, or multi-circuit cold plates)
Number of circuits (7 circuit cold plate, 8 circuit cold plate, 10 circuit cold plate)
Inlet/outlet positions and thread standards
Surface flatness and mounting features
Custom designs ensure optimal cold plate cooling performance for your system.
Brazed liquid cold plates support various internal structures, including:
Microchannel cold plate / micro channel cold plate for high heat flux
Parallel flow channels for uniform temperature distribution
Serpentine or multi-pass designs for controlled pressure drop
High-flow designs for water cooled cold plate applications
Channel selection depends on thermal load, flow rate, and pumping capacity.
Typical coolants for brazed liquid cold plates include:
Deionized water
Water-glycol mixtures
Industrial coolants compatible with aluminum or stainless steel
Coolant compatibility is critical, especially for aluminum cold plates, to prevent corrosion and maintain long-term reliability.
Brazed liquid cold plates are widely used in:
Data center CDU and liquid cooling distribution systems
Energy storage and battery thermal management
Electric vehicles and automotive power electronics
Industrial inverters and power supplies
High-power laboratory equipment and lab cold plates
They are especially suitable where high reliability and consistent cold plate cooling are required.
A microchannel cold plate refers to channel size rather than manufacturing method. Brazed liquid cold plates can incorporate microchannel structures, combining both benefits:
Microchannel design for enhanced heat transfer
Brazed construction for structural strength and leak resistance
This combination is commonly used in high-density liquid cooling plates for electronics.
Yes. Due to the brazed internal structure, brazed liquid cold plates can withstand higher operating pressures compared to mechanically sealed or tubed cold plates, making them suitable for industrial liquid cooling systems and refrigerated cold plate applications.
Kingka Tech Industrial Limited
We specialize in precision CNC machining and our products are widely used in telecommunication industry, aerospace, automotive, industrial control, power electronics, medical instruments, security electronics, LED lighting and multimedia consumption.
Address:
Da Long New Village, Xie Gang Town, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province, China 523598
Email:
Tel:
+86 137 1244 4018