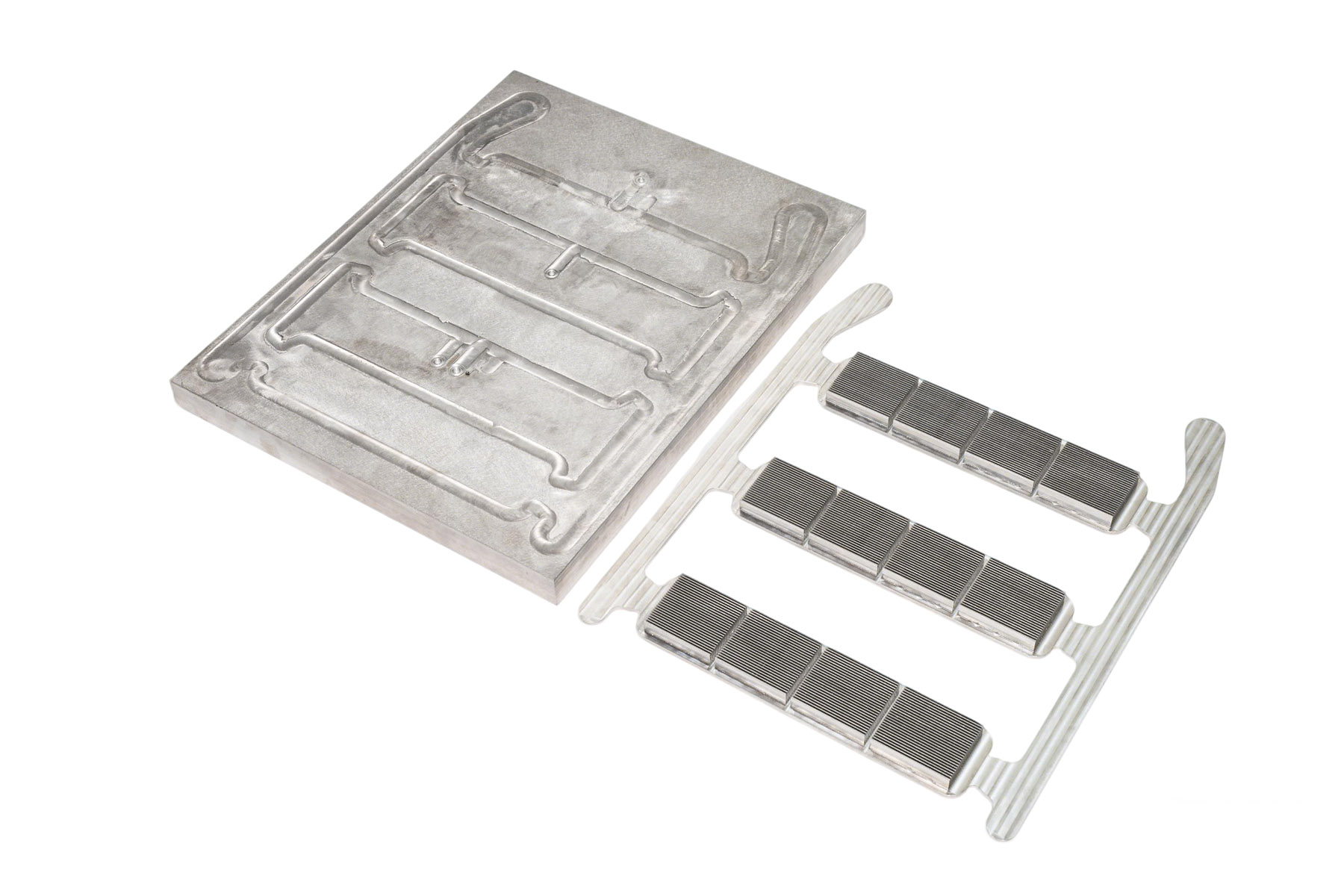
As high-power electronics continue to evolve across industries such as data centers, electric vehicles, energy storage, and high-performance computing, thermal management has become a critical factor in system reliability and efficiency. Traditional air cooling solutions are increasingly insufficient for today’s high heat flux applications. As a result, the liquid cold plate, also known as a liquid cooled heat sink, has become a core component of modern cold plate cooling systems.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of Liquid Cold Plate technology, covering working principles, typical cold plate types, manufacturing challenges, and advanced joining processes. It is intended to help engineers and decision-makers better understand cold plate liquid cooling solutions and select the most suitable approach for their applications.

1. What Is a Liquid Cold Plate?
A liquid cold plate (also referred to as a liquid cooling plate or water cooling cold plate) is a heat transfer device that removes heat from high-power components by circulating coolant through internal channels.
The basic working principle of cold plate cooling is as follows:
Heat is generated by electronic components such as CPUs, GPUs, power modules, or batteries
Heat is conducted from the device into the cold plate Heat Sink through direct contact
Coolant flows through internal channels, absorbing and carrying away heat
The heated liquid is transferred to an external heat exchanger for dissipation
Compared with air cooling, water cooling plates offer:
Higher heat transfer efficiency
More uniform temperature distribution
Compact system integration
Superior performance for high heat flux environments
In computing applications, the same principle is applied in CPU water blocks, CPU cooling blocks, and GPU with waterblock designs, where a compact water block directly cools processors.
2. Typical Liquid Cold Plate Types and Their Challenges
Different applications require different liquid cold plate structures. Material selection, internal channel design, and manufacturing methods directly impact performance, cost, and reliability.
2.1 Tube-in-Plate Liquid Cold Plate

Tube-in-plate designs embed metal tubes into a base plate to form coolant channels.
Advantages:
Challenges:
Limited channel density reduces cooling efficiency
Multiple thermal interfaces increase thermal resistance
Copper tube and aluminum plate combinations may cause galvanic corrosion
Not suitable for high-performance cold plate cooling systems
2.2 Gun-Drilled Liquid Cooling Plate
Gun drilling creates straight internal channels inside a solid metal plate, which are then sealed at the ends.
Advantages:
Challenges:
Straight channels limit design flexibility
Difficult to manufacture plates longer than 500 mm with high precision
End plugs are potential leakage points
Less suitable for complex thermal layouts
2.3 Brazed Liquid Cold Plate

A brazed liquid cold plate is produced by machining flow channels into a base plate and permanently joining a cover plate through vacuum brazing.
Advantages:
Enables complex internal channel designs
Excellent thermal performance
Uniform temperature distribution
Commonly used in high-end liquid cold plate cooling systems
Challenges:
Requires expensive vacuum brazing furnaces
Long production cycles (6–8 hours per batch)
High sensitivity to surface cleanliness and process control
Higher manufacturing cost and limited flexibility
2.4 Embedded Tube Cold Plate
In this design, bent tubes are pressed, brazed, or bonded into a base plate.
Advantages:
More flexible channel routing than surface-mounted tubes
Compatible with aluminum, copper, or stainless steel tubes
Challenges:
3. Liquid Cold Plate Manufacturing Process Comparison
The performance and reliability of a liquid cooling plate depend heavily on its joining and sealing technology. Different manufacturing methods offer distinct trade-offs.
3.1 Common Joining Technologies
| Process | Key Features | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|
| Vacuum Brazing | High-temperature metallurgical bonding | Complex designs, high performance | High cost, long cycle time |
| Friction Stir Welding (FSW) | Solid-state welding | Leak-free, high strength, low distortion | Requires specialized equipment |
| Soldering | Low-temperature joining | Low initial investment | Limited strength, not for high pressure |
| O-Ring Sealing | Mechanical sealing | Easy maintenance | Aging risk, long-term reliability issues |
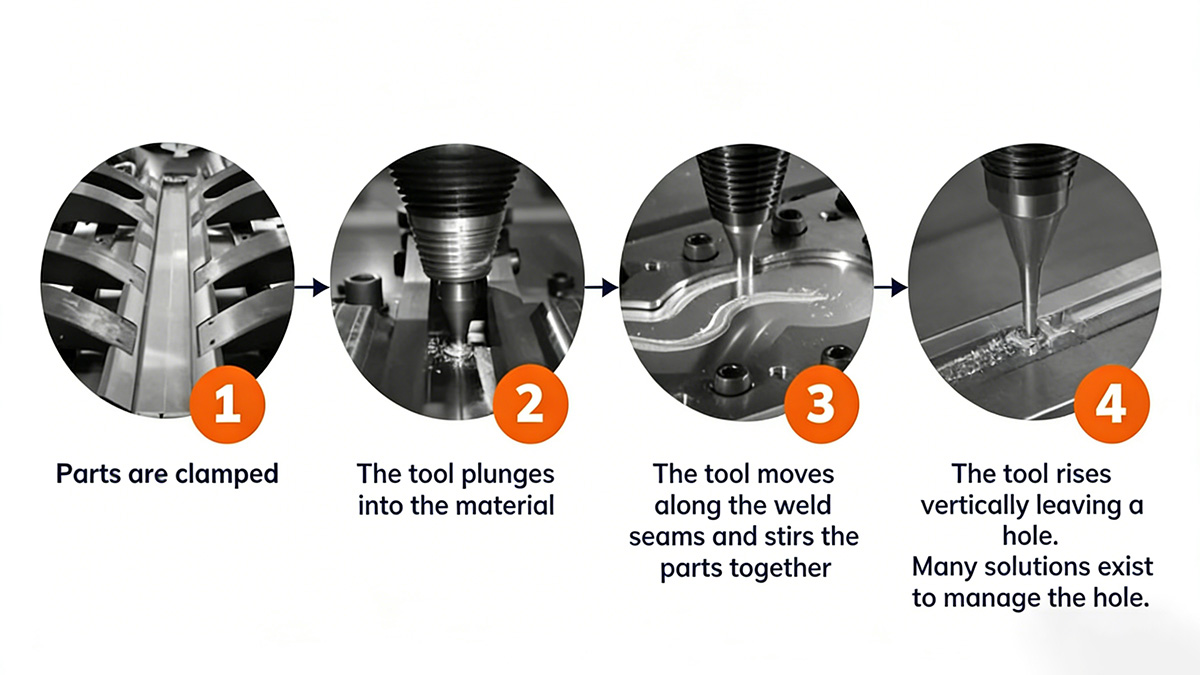
3.2 Friction Stir Welding for Liquid Cold Plates

Friction Stir Welding (FSW) is a solid-state joining process that produces heat through mechanical friction rather than melting the material.
Key advantages for liquid cold plate manufacturing include:
No melting, preserving original thermal conductivity
Dense, void-free welds with near-zero leakage risk
High mechanical strength, close to base material
Short welding cycles, ideal for automation
Manufacturing costs 2–10 times lower than brazing
FSW is increasingly adopted for OEM liquid cold plates, ODM liquid cooling plates, and high-volume custom cold plates.
4. Application Scenarios
Liquid cold plates are widely used in applications requiring high-performance thermal management, including:
Data centers and servers (CPU cooling block, best CPU water block solutions)
AI accelerators and GPU with waterblock systems
Electric vehicle power electronics
Battery packs and energy storage systems
Telecom equipment and 5G infrastructure
Industrial power supplies and inverters
5. Key Factors When Choosing a Liquid Cold Plate
When selecting a custom liquid cold plate, the following factors should be evaluated:
Heat load and heat flux density
Coolant type and operating pressure
Environmental conditions
Reliability and lifespan requirements
Cost targets and production volume
Customization and integration needs
Working with an experienced liquid cold plate manufacturer ensures optimal balance between performance, reliability, and cost.
The liquid cold plate is a critical component in modern cold plate liquid cooling systems. While traditional solutions such as tube-in-plate and gun-drilled designs remain viable for certain applications, advanced processes like vacuum brazing and friction stir welding are driving the industry forward.
Among these, friction stir welded liquid cooling plates offer the best balance of:
Thermal performance
Mechanical strength
Leak-free reliability
Cost efficiency
As demand for high-performance cooling continues to rise, custom cold plates, OEM liquid cold plates, and ODM liquid cooling plates will play an increasingly important role in next-generation thermal management solutions.