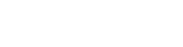In the era of high-density computing, traditional air-cooling systems are rapidly being replaced by advanced liquid cooling architectures. At the core of this transformation lies the Data Center Cooling Distribution Unit (CDU)—a critical system component responsible for the precise delivery and regulation of coolant throughout the server infrastructure.

Definition: What Is a Data Center Cooling Distribution Unit (CDU)?
A Cooling Distribution Unit (CDU) is the central distribution device in liquid-cooled data centers, delivering coolant—either water or fluorinated fluids—to cold plates, immersion cooling tanks, or direct-to-chip water blocks. The CDU ensures targeted heat removal at chip-level or rack-level, enhancing thermal efficiency and reliability across modern data centers.
Key Functions of CDU Systems
Coolant Distribution: Controls flow using pumps and valves to ensure balanced cooling for each server.
Temperature & Pressure Control: Maintains coolant temperature within a tight tolerance range (±0.5°C) and ensures stable pressure to prevent cavitation or leakage.
Redundancy Design: Employs dual-pump and dual-power configurations to ensure 99.999% availability.
Real-time Monitoring: Integrates with DCIM systems to provide live feedback on flow rates, temperatures, and leakage status.
Types of Data Center Cooling Distribution Units
Rack-level CDU: Designed for single cabinet use, supporting 30-100kW cooling capacity. Ideal for scalable and flexible deployments.
Row-level CDU: Services an entire row of server racks with power support up to 500kW, ideal for high-density compute clusters.
Immersion CDU: Specifically engineered for single-phase or two-phase immersion cooling systems, compatible with fluorinated fluids like 3M Novec.
Advantages of CDU Liquid Cooling Systems
Achieves a Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) as low as 1.05, saving 30%+ energy over air cooling.
Supports ultra-high-density workloads (e.g., 50kW+ per rack for AI or GPU servers).
Operates silently with fanless CDU designs (<50dB noise level).
Application Scenarios
Supercomputing Facilities (e.g., Japan's Fugaku)
AI Training Clusters (e.g., NVIDIA DGX A100)
Edge Data Centers with compact CDU footprints
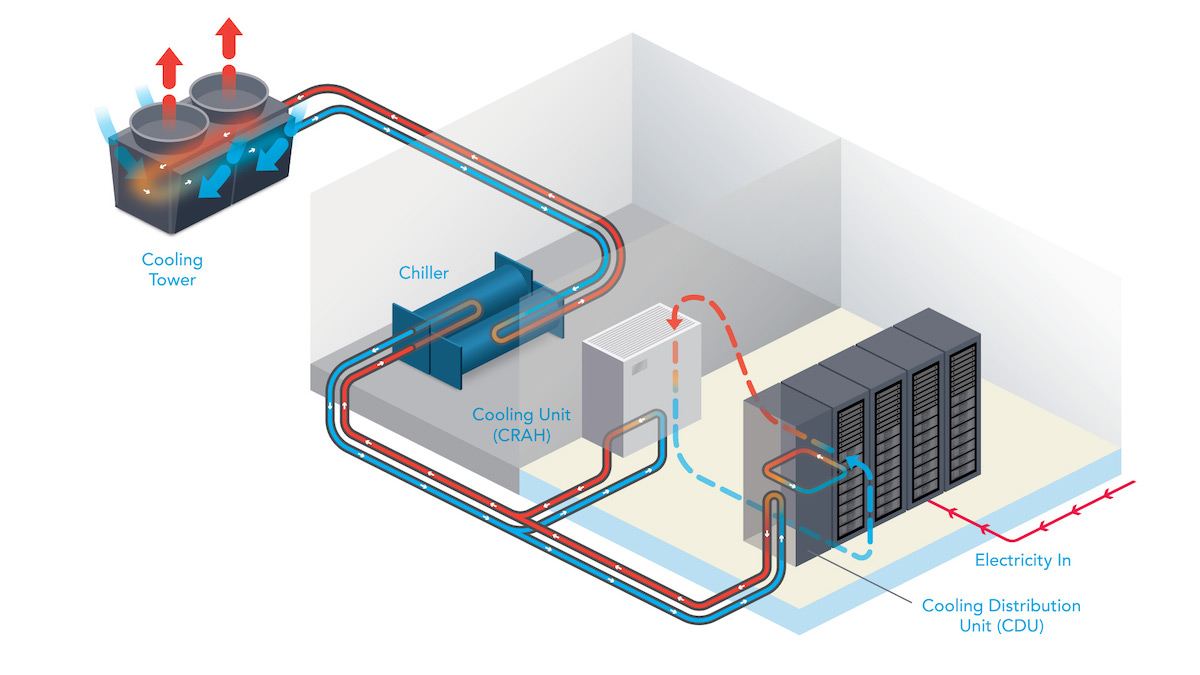
Cold Plates, heat sinks, and Water Blocks: The Execution Layer of CDU Cooling
While the CDU serves as the command center for liquid flow, its true cooling potential is realized through its terminal components: CDU water-cooled cold plates, Heat Sinks, and water blocks. These components directly interface with heat-generating devices to execute efficient thermal transfer.
| Component | CDU System Role | Application |
|---|
| Cold Plate | Transfers coolant to chips via microchannels for precise heat removal | GPU/CPU-intensive racks, AI compute nodes |
| Heat Sink | Provides secondary cooling to CDU's internal electronics | CDU control cabinet (pumps, PSU modules) |
| Water Block | Customized cooling of irregular thermal sources; connects with CDU pipes | HPC systems, supercomputing accelerators |
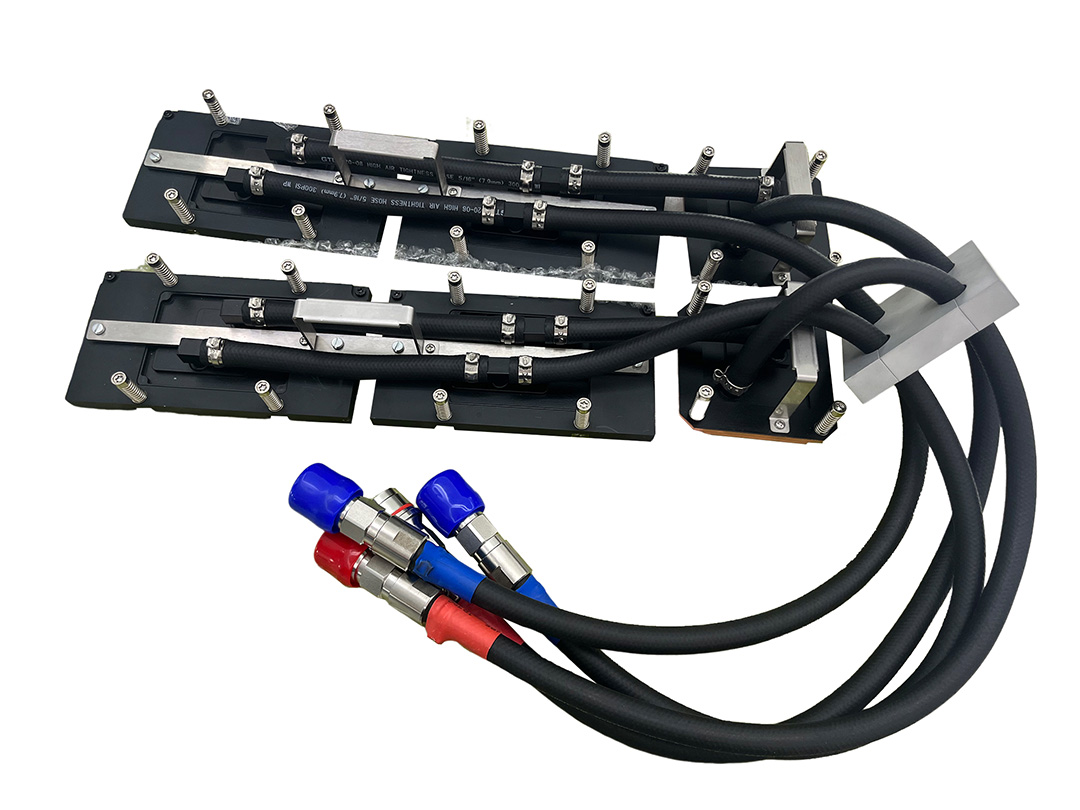

Technical Advantages vs. Traditional Air Cooling
1. Cold Plates (CDU Water Plates)
Extreme Heat Flux Capacity: Supports up to 500–1000W/cm², outperforming air cooling (50–100W/cm²).
Surface Uniformity: Delivers thermal spread with <2°C delta across the plate, preventing local overheating.
Smart CDU Integration: Built-in sensors feed real-time data to CDU controllers, enabling dynamic flow and temperature regulation.
2. Heat Sinks for CDU Internal Components
CDU Self-Cooling: Ensures CDU reliability by passively cooling key electronics.
Lightweight Design: Aluminum 6063 construction minimizes weight, ideal for rack-mount CDU units.
3. Custom Water Blocks (CDU Water Block Solutions)
Complex Shape Compatibility: CNC or 3D-printed to match non-standard chip designs (e.g., NVIDIA H100).
Low Flow Resistance: Engineered water channels reduce CDU pump workload (pressure drop < 0.3 bar).
CDU-Component Synergy: Smart Thermal Management
Modern CDU liquid cooling systems are not standalone—they function in harmony with cold plates, heat sinks, and water blocks to form a dynamic, closed-loop thermal architecture. Key highlights include:
Dynamic Flow Tuning: CDU adjusts coolant delivery based on feedback from water plates or water blocks (e.g., via Intel DCM protocol).
Leak Protection: Quick-disconnect fittings (e.g., CPC, QD) on water blocks and CDU hoses ensure sealed, safe connections.
Energy Efficiency: Combined CDU + cold plate architecture can achieve PUE as low as 1.05, compared to 1.5+ for traditional systems.
Real-World Applications
Google Data Center: Utilizes CDUs to distribute chilled water to rack-mounted water plates for TPU cooling.
Tesla Dojo Supercomputer: Employs CDU-integrated custom water blocks to manage 1MW per cabinet.
Crypto Mining Farms: Use aluminum cold plates + CDU instead of fans, reducing power consumption by 30%.
Future Trends in CDU-Based Cooling Solutions
Two-Phase CDU Cooling: Uses phase-change fluids like liquid nitrogen to achieve 5x efficiency gains.
AI-Driven CDU Control: Enables predictive adjustments in flow and temperature based on workload forecasting.
As the backbone of next-generation data center infrastructure, the Data Center Cooling Distribution Unit (CDU)—along with advanced CDU water plates, heat sinks, and liquid cooling water blocks—will continue to evolve toward smarter, quieter, and more efficient thermal management solutions.
Keyword Summary: Data center Cooling Distribution Unit (CDU), CDU water plate, CDU water block, immersion CDU, rack-level CDU, cold plate, heat sink, liquid cooling system, full-chain liquid cooling, water-cooled server, AI liquid cooling.